Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) is a web service that provides secure, resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It is designed to make web-scale cloud computing easier for developers.
EC2 represents Elastic Cloud Compute.
Here Compute means we are requesting AWS to provide a compute instance comprising CPU,RAM and DIsk. We are eventually requesting for Virtual Server.
Here cloud means we are getting a cloud virtual machine.
Elastic here is used with the service to determine that the service can be scaled up or down which means it is elastic in nature.
So here EC2 is the virtual machine/server or a compute system over a cloud given by AWS
Advantage of EC2
Imagine we have our own servers and we create our own virtual machines. These will be in number of thousands. But after creating we have to upgrade this virtual machines, check security issues ,multiple crashes. This can be a tedous task. Instead AWS takes care of all this and provide us the virtual machine.This will also reduce the cost.
Types of EC2 instance
General purpose EC2 Instance
These EC2 instance provide balance of compute , memory and network resources. These can be used for a variety of diverse workloads like webservers.
Compute Optimised EC2 Instance
These are used for applications requiring high performance processing
Storage Optimised EC2 Instance
These are used for applications that require high, sequential read-and-write access to large datasets
Memory Optimised EC2 Instance
These Memory Optimized instances are designed to handle memory-intensive workloads
Accelerated EC2 Instance
Accelerated computing instances use hardware accelerators, or co-processors, to perform functions, such as floating point number calculations, graphics processing, or data pattern matching, more efficiently than is possible in software running on CPUs.
AWS EC2 Regions and Zones
Amazon EC2 is hosted in multiple locations world-wide. Each Region is a separate geographic area. Availability Zones are multiple, isolated locations within each Region. Each Region is designed to be isolated from the other Regions. This achieves the greatest possible fault tolerance and stability.
Creating EC2 Instance
Login into AWS console as root user
Search for EC2 in search bar

Click on Instances
Then click on Launch Instance at right hand side
Name the Web server, and choose the OS Image as Ubunutu. Choose instance type as Free Tier.

Create a new Key Login Pair .
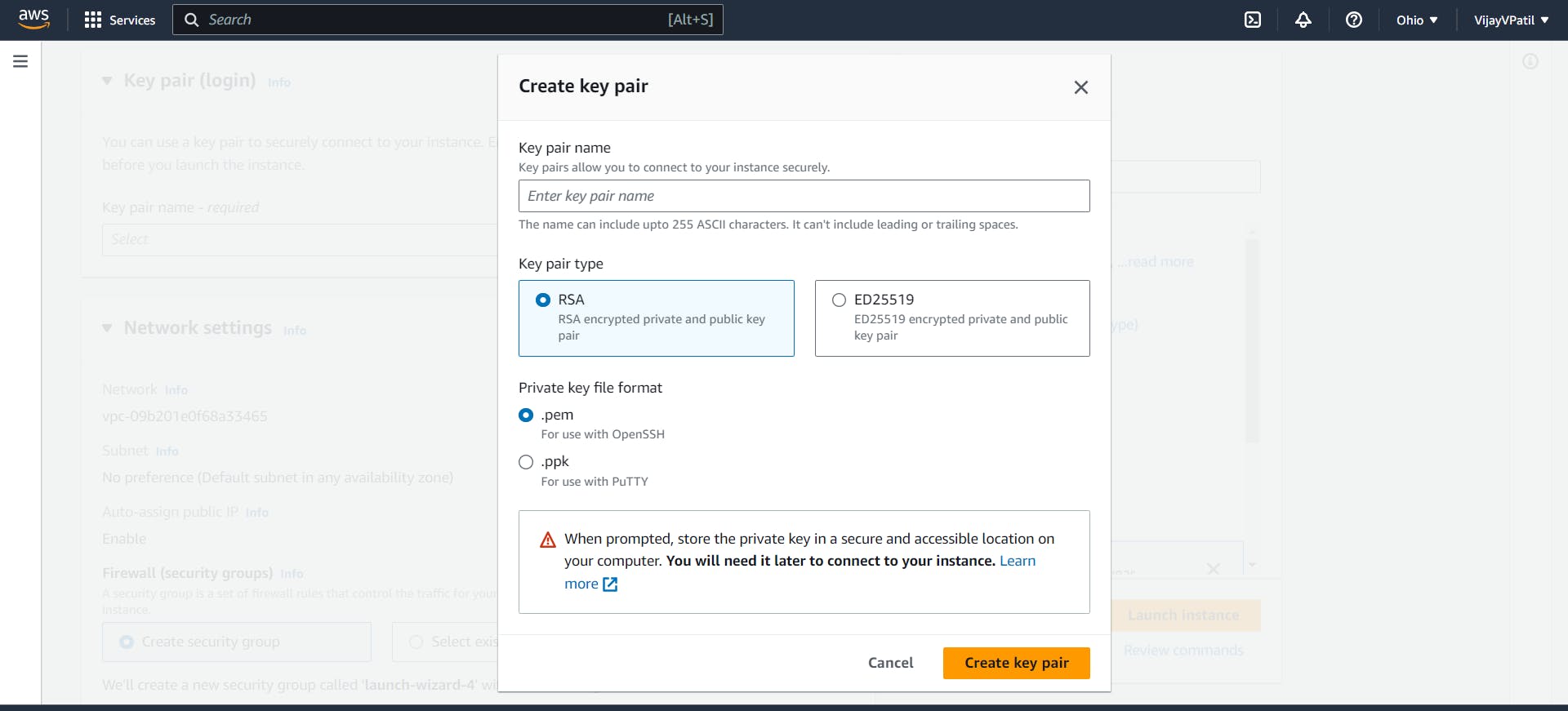
Remember we need this to access our instance via terminal. This is a key value pair. It is a combination of public private key. Instance have public key and we need private key to login. Name the Key pair name and keep default settings. A pem file will be downloaded. Keep it in an accessible location.
Keep other settings as it is and click on Launch Instance. Within couple of minutes we will get our instance running.
Now navigate back to Instances and click on Instance ID. We will have public and private ip address. We will use public ip address to login into instance
Login to EC2 instance via Terminal
Download Mobaexterm or Putty.
Launch the application(Download Mobaexterm or Putty)
I have my pem file in downloads. So I ran below command and after @ I used my public IP address from console. I changed the permission of the file.
```plaintext 04/07/2023 20:12.18 /home/mobaxterm chmod 600 C:/Users/vijay/Downloads ✓
04/07/2023 20:13.06 /home/mobaxterm ssh -i C:/Users/vijay/Downloads/test42.pem ubuntu@3.135.208.138 Welcome to Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.19.0-1025-aws x86_64)
- Documentation: help.ubuntu.com
- Management: landscape.canonical.com
Support: ubuntu.com/advantage
System information as of Tue Jul 4 14:43:13 UTC 2023
System load: 0.0078125 Processes: 98 Usage of /: 20.8% of 7.57GB Users logged in: 0 Memory usage: 25% IPv4 address for eth0: 172.31.10.245 Swap usage: 0%
Expanded Security Maintenance for Applications is not enabled.
0 updates can be applied immediately.
Enable ESM Apps to receive additional future security updates. See ubuntu.com/esm or run: sudo pro status
The list of available updates is more than a week old. To check for new updates run: sudo apt update
Last login: Tue Jul 4 14:42:12 2023 from 103.66.214.251 To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo ". See "man sudo_root" for details.
ubuntu@ip-172-31-10-245:~$
4. And now we are inside ubuntu.
## Deploy Jenkins on AWS
1. Beforehand we need to update packages in Ubuntu.
```plaintext
sudo apt update
Now we need to instal Java
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jdkTo check if java is installed or not
java --version
If it return below output then it is installed

Visit Jenkins official website-> Download -> Ubuntu. Copy the command in Weekly release section and run it.
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee \ /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \ https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian binary/ | sudo tee \ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install jenkinsTo check if jenkins is installed or not run below command
ubuntu@ip-172-31-10-245:~$ sudo systemctl status jenkins
The port number of Jenkins is 8080. We need to open the port 8080 so that we can access Jenkins through EC2 server.
Click on id of our instance.
Navigate to Security tab
Click on security group -> Inbound traffic rules -> Edit inbound rules
Add a new rule

And Save the rule
Now run the URL in browser
http:// <YOUR_PUBLIC_IP_ADDRESS> :8080
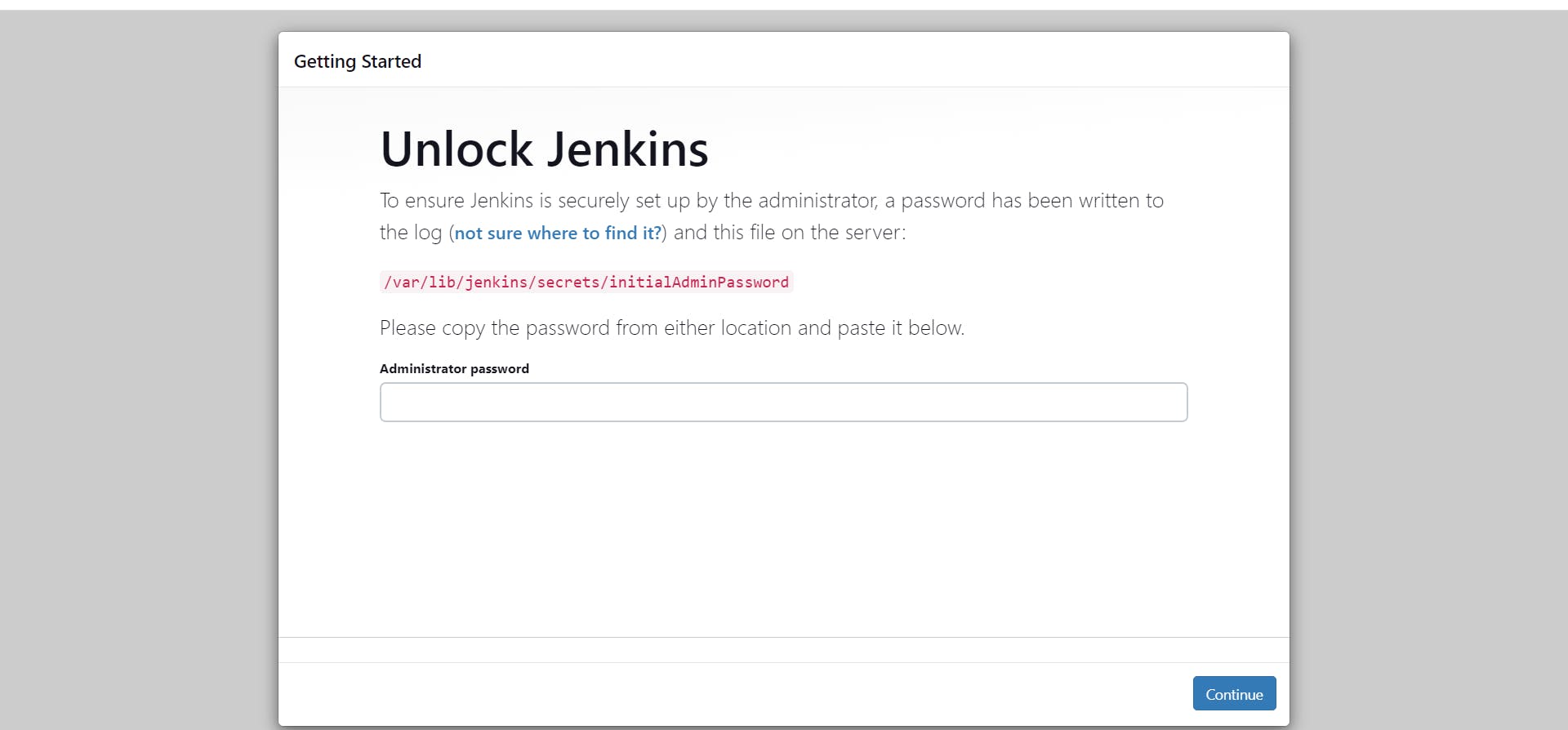
This will show that jenkins is accessible .
